What is a Plastic Injection Mold and How Does It Work?
A plastic injection mold is essential in modern manufacturing. It shapes plastic into intricate designs. This process transforms raw plastic pellets into final products. Understanding how this mold works reveals its significance in various industries.
The plastic injection mold operates through a straightforward method. First, plastic granules are heated until they melt. Then, the molten plastic is injected into the mold cavity. After cooling, the mold opens, revealing the final product. This efficiency is crucial for mass production.
However, making a plastic injection mold requires precision and skill. Designers must consider the size, shape, and material. Any errors can lead to defects. These challenges offer opportunities for reflection and improvement in the design process. As technology advances, the methods of creating molds and the types of plastics used continue to evolve. The journey of a plastic injection mold is both fascinating and complex.
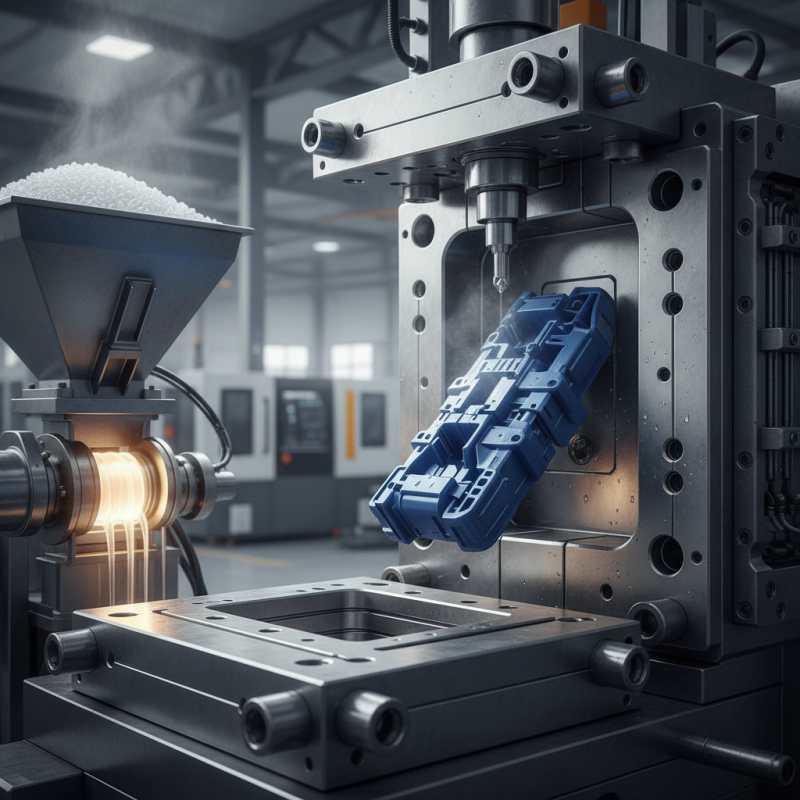

What is Plastic Injection Molding?
Plastic injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process. It allows for the creation of items from plastic materials. This technique involves melting plastic and injecting it into a mold. Once the plastic cools, it hardens into the shape of the mold. This process is efficient and can produce complex shapes with high precision.
Molding can be applied to various materials. Polyethylene and polystyrene are common choices. Different plastics offer different properties, which can be tailored for specific needs. This adaptability makes injection molding popular across many industries.
**Tip:** Always consider the material's properties before choosing. Each type serves a unique purpose.
However, challenges can arise in this process. Molds can be expensive to create. Their design requires careful planning to avoid errors. Simple mistakes can lead to wasted material and time.
**Tip:** Prototype with smaller batches. This approach helps to catch issues early.
Efficiency remains key, but quality cannot be overlooked. A balance is essential. Regular maintenance of molds can avoid production delays. Investing time in refining processes can lead to better outcomes.
Plastic Injection Molding Process Overview
The Components of a Plastic Injection Mold
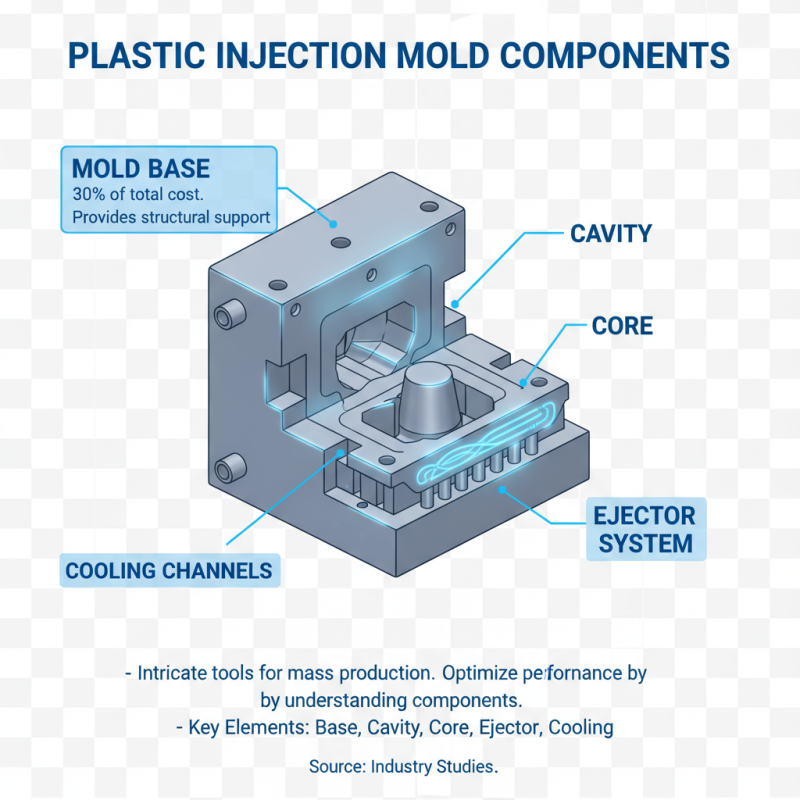
Plastic injection molds are intricate tools used in mass production. Understanding their components is essential for optimizing their performance. Each mold typically consists of critical elements including the mold base, cavity, core, ejector system, and cooling channels. The mold base provides the main structural support, holding everything in place. According to industry studies, the mold base accounts for about 30% of the total mold cost.
The cavity and core shapes dictate the final product's design. Precision in these components is vital for efficient production. Even a small deviation can lead to defects, causing delays and increased costs. Research indicates that up to 20% of production issues stem from mold imperfections. The ejector system plays a crucial role here, ensuring smooth release of the molded part. However, if not carefully designed, it can damage the product or the mold itself. Cooling channels manage temperature during the injection process. Inefficient cooling can lead to longer cycle times and lower quality.
Many manufacturers overlook these details, focusing instead on output quantity. A balanced approach is needed. Investing in high-quality components can reduce long-term costs. A report from a leading industry analysis firm highlights that proper mold maintenance can improve lifespan by over 50%. Reflecting on these components reveals the complexity behind plastic injection molding. Addressing imperfections can enhance productivity and quality.
How the Plastic Injection Molding Process Works
The plastic injection molding process transforms raw plastic into various products. It starts with heating plastic granules until they melt. This molten plastic is then injected into a mold under high pressure. The mold is designed to create the desired shape of the final product. Once the plastic cools, it solidifies and takes on the shape of the mold.
During this process, precision is crucial. Even small variations can affect the final product. The cooling time is another factor that needs attention. If it's too short, the plastic might not form properly. If too long, production slows down. It's a balancing act that requires careful monitoring. Operators must regularly check equipment and parameters. They need to be vigilant to avoid defects.
Unfortunately, not all products come out perfectly. Issues like air traps or incomplete fills can occur. These imperfections call for further adjustments. A successful molding operation requires constant reflection and improvement. Regular training for staff is also important. It can help address recurring problems and enhance overall efficiency.
What is a Plastic Injection Mold and How Does It Work?
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| Mold Material | Typically made from steel or aluminum, chosen for durability and thermal conductivity. |
| Mold Types | Single cavity, multi-cavity, family molds, and hot runner or cold runner systems. |
| Injection Pressure | Typically ranges from 500 to over 30,000 psi depending on material and part complexity. |
| Cycle Time | The time it takes to complete one injection cycle, usually between 15 seconds to a few minutes. |
| Tolerances | Typically ±0.005 inches, but can vary based on material and part design. |
| Applications | Used for producing a wide variety of products such as containers, automotive parts, and electronic housings. |
| Common Materials | Includes ABS, polycarbonate, nylon, and polyethylene, among others. |
Applications of Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding is widely used across various industries. This method produces durable and intricate plastic parts. From automotive components to medical devices, its applications are vast. Manufacturers rely on this technique for consistent quality and efficiency.
In the automotive sector, plastic injection molding shapes everything from dashboards to exterior panels. These parts are lightweight yet strong, enhancing vehicle performance. In the healthcare industry, precision is crucial. Components for devices like syringes and inhalers must meet strict standards. Molding technology allows for these specific requirements to be met efficiently.
Tip: Always consider material selection. The right choice can improve product longevity and functionality. Testing prototypes is vital. Even small defects can lead to significant failures in end products. Regularly updating molds is also important. Wear and tear can affect production quality over time. Keep revisiting your processes to minimize imperfections.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Plastic Injection Molding
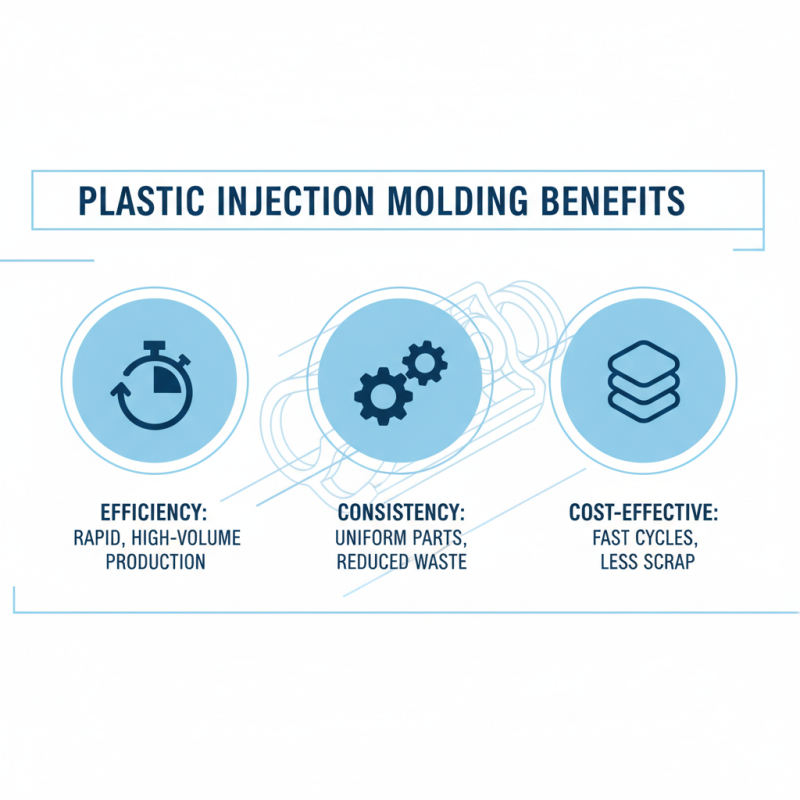
Plastic injection molding is a popular manufacturing process. It offers several advantages. One major benefit is efficiency. The process can produce large quantities of parts quickly. Each cycle can take only a few seconds, making it ideal for high-volume production. Consistency is another advantage. Every piece produced is nearly identical in shape and size, which reduces waste.
However, there are some disadvantages to consider. The initial cost of creating a mold can be quite high. This expense may not be justified for smaller production runs. Another issue is design limitations. Complex designs can be challenging and may require additional engineering work. Moreover, once the mold is made, modifying it can be difficult and expensive. It's important to weigh these factors before committing to this manufacturing method.
Related Posts
-
Exploring Innovations in Plastic Injection Molds at the 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-

Unlocking Industry Potential with Plastic Mold Innovation at the 138th Canton Fair 2025
-

Exploring the Benefits of Home Plastic Injection Molding: A Deep Dive into Efficiency and Innovation
-

How to Choose the Right Injection Mold Inserts for Your Manufacturing Needs
-

2025 How to Choose the Right Injection Tooling for Your Manufacturing Needs
-

Top 10 Injection Tooling Techniques for Optimal Manufacturing Efficiency








