What is Plastic Injection Molded Parts and How Are They Made?
Plastic injection molded parts play a crucial role in modern manufacturing. Experts like Dr. Emily Chen, a leading authority in polymer science, state, “The efficiency of plastic injection molding transforms ideas into tangible products.” This process involves injecting molten plastic into molds to create precise parts for various applications.
The journey of creating plastic injection molded parts begins with design. Engineers must carefully plan each detail. The choice of materials is vital, affecting strength and flexibility. Once the design is set, molds are manufactured. This step requires precision and skill to ensure quality.
While plastic injection molding is efficient, it’s not without challenges. Maintaining quality across batches can be difficult. Small variations in temperature or pressure can lead to defects. Continuous improvement is necessary, as the industry evolves and faces new demands. Balancing speed and quality in producing these parts is essential for success.
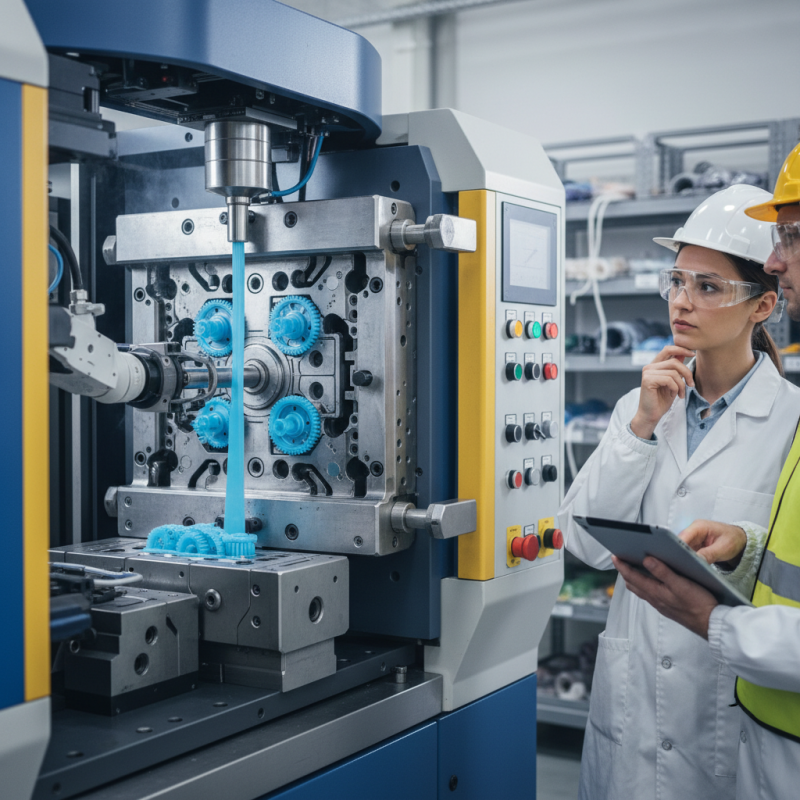

Definition of Plastic Injection Molded Parts
Plastic injection molded parts are widely used in various industries. These components are created through a process that involves injecting molten plastic into a mold. The molds are typically made of metal and are designed to create specific shapes. Once the plastic cools and solidifies, it takes on the form of the mold, resulting in precise and complex shapes.
These parts can range from simple items to intricate designs. Common examples include containers, automotive parts, and medical devices. The versatility of injection molding makes it a go-to method for manufacturers. However, not all designs translate perfectly into molded parts. Sometimes, issues arise during production. Warping, incomplete filling, or surface defects can occur. These challenges require careful planning and adjustment.
Designing for injection molding requires attention to detail. Every angle, size, and curve needs consideration. Small mistakes can lead to significant problems during production. Even skilled designers must iterate their work. Mistakes become learning opportunities. Each design reflects not only functionality but also the need for continuous improvement. The journey of creating plastic injection molded parts is indeed a blend of innovation and reflection.
What is Plastic Injection Molded Parts and How Are They Made?
This chart illustrates the percentage usage of various materials in plastic injection molding, highlighting the diversity of materials that can be molded into parts.
Overview of the Injection Molding Process
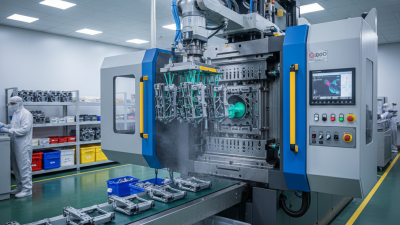
The injection molding process is a widely used method for creating plastic parts. It starts with raw plastic pellets, which are heated until they become liquid. The liquid material is then injected into a mold under high pressure. This initial step might seem straightforward, yet it demands precision and control.
After the plastic is injected, it cools and solidifies into the desired shape. The mold opens, and the finished part is ejected. This process can produce complex shapes with high accuracy and minimal waste. However, the design of the mold can be challenging. Creating a mold that meets all specifications while allowing for easy part removal is no small feat.
Quality control is crucial throughout this process. Even small errors can lead to defects in the final product. Engineers often need to adjust temperatures and pressures carefully. Sometimes, unexpected results force them to revisit the design phase. This reflection can lead to better practices in future projects.
What is Plastic Injection Molded Parts and How Are They Made? - Overview of the Injection Molding Process
| Dimension | Value |
|---|---|
| Material Types | ABS, Polycarbonate, Nylon |
| Typical Thickness | 0.5 mm to 5 mm |
| Cycle Time | 15 to 120 seconds |
| Tolerances | ±0.1 mm to ±0.5 mm |
| Applications | Automotive, Medical Devices, Consumer Products |
| Common Finishes | Glossy, Matte, Textured |
| Cost Factors | Material cost, Mold complexity, Production volume |
| Environmental Considerations | Recyclability of materials, Waste management |
Materials Used in Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding relies heavily on the choice of materials used in the process. The most common materials include thermoplastics. These are versatile and can be melted and reshaped multiple times, allowing for a range of applications. Polypropylene and polystyrene are popular choices in various industries. They are lightweight, durable, and come in diverse colors.
Another notable material is thermosetting plastics. Unlike thermoplastics, these materials undergo a chemical change when heated and cannot be remolded. This provides strength and heat resistance, making them ideal for specific uses. The selection of materials can significantly impact the part's final properties, such as rigidity or elasticity.
However, processing these materials requires careful consideration. Misjudging the temperature can result in defects. Variations in material quality can also lead to inconsistencies. Each type of plastic behaves differently under pressure and heat. Understanding these nuances is essential. The challenge lies in balancing these factors for optimal results while striving for improvement in the manufacturing process.
Steps Involved in Manufacturing Injection Molded Parts
Plastic injection molding is a popular manufacturing method for producing various parts. The process involves several key steps, each contributing to the final product's quality.
The first step is designing the part. Engineers create detailed blueprints that outline dimensions, material specifications, and functional requirements. Next, mold fabrication comes into play. The mold is crafted from high-grade steel or aluminum. This step requires precision, as any flaw can lead to defects in the molded parts. After the mold is ready, it's mounted in an injection molding machine.
The actual molding process follows. Plastic pellets are heated until they melt and then injected into the mold. This stage is crucial, as the temperature and pressure must be carefully controlled. Cooling follows, allowing the plastic to solidify. Sometimes, cooling times can be too lengthy or too short, leading to complications. Finally, the mold opens, and the part is ejected. Inspecting for defects is essential, as some imperfections might not be immediately visible. The process can yield numerous perfect parts or lead to various challenges that warrant adjustments for future runs.
Applications and Benefits of Plastic Injection Molded Components

Plastic injection molded parts play a crucial role in various industries. They are widely used in automotive, consumer goods, and electronics. These components are produced by injecting molten plastic into molds, which shape the final product. The versatility of this manufacturing method allows for complex shapes and high production rates.
Applications are vast. In the automotive sector, lightweight plastic parts reduce fuel consumption. Consumer goods such as toys benefit from colorful, durable designs. Electronics often use plastic for housing and components. However, not all applications yield perfect results. Sometimes, defects occur due to improper mold design or material choices.
Benefits include cost-effectiveness and efficiency. Large production runs can be more affordable. Yet, the initial investment for molds can be high. This leads to a potential risk for small businesses. Balancing quality and cost is a constant challenge. Each project needs careful planning to avoid pitfalls.
Related Posts
-

Understanding the Process and Advantages of Plastic Injection Molded Parts in Modern Manufacturing
-

Understanding the Plastic Injection Moulding Process: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
-

Exploring the Future of Plastic Components: Innovations and Sustainability in Modern Manufacturing
-
What is Injection Molded Parts and How They are Made
-

Why Choose Home Plastic Injection Molding for Your DIY Projects?
-

How to Choose the Right Plastic Injection Tooling for Your Project?








